Antimicrobial Compositions and Combination Therapies
Compositions and methods to combat drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
Antibiotic resistance is an urgent and growing health threat. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is known to cause a variety of infections in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals, but especially the latter. It utilizes both intrinsic and acquired resistance to counter most antibiotics. Further, formation of multidrug-tolerant persister cells present a major treatment challenge and are believed to be responsible for relapse and chronic infections. Identification and development of novel antimicrobial agents and strategies able to target such cells is an emerging and critical need.
This jointly owned (University at Buffalo and Cleveland State University) invention provides compositions and methods that have demonstrated synergistic antimicrobial effects on otherwise drug-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including against persister cells (see figure below involving a metallo-ß-lactamase strain).
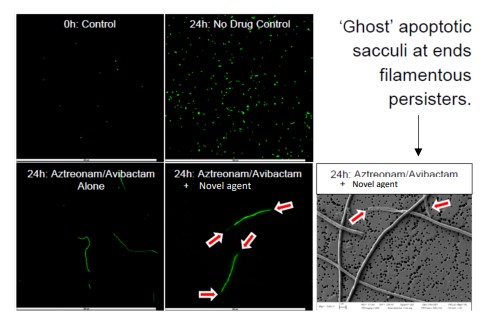
- Effective against drug resistant strains
- Synergistic with traditional antimicrobial agents
- Effective against persister cells
US National patent 19/125,801 filed April 30, 2025
In vitro.
Available for licensing or collaboration.
No publications to date.
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
Patent Status |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |
|