Wearable Gait Lab Sensor System
A wearable underfoot force sensing insole provides data for balance ability analysis and balance test scoring.
- Data are needed for improving clinical outcomes and decreasing the entire cost of rehabilitation care, fall risk evaluation/prevention, and stroke rehab.
- US market for total knee and hip joint replacement: ~1 million procedures (2018); expected to increase to 3.5 million procedures/year over the next 10 years.
- Sensory devices have the potential to impact monitoring balance tests and providing quantitative supports for activity analysis. The Wearable Gait Lab system has been developed to monitor activities of legs and feet during static and dynamic balance tests. In this system, a wearable underfoot force sensing unit in the form of a wearable insole, is used to record motions of the feet and plantar pressure data; a joint angular and EMG (electromyographic) sensing unit is used to record leg motions and muscular data; and an android application is implemented to control all units, monitor data recording process, and upload recorded data to a cloud server, which allows medical professionals to review it remotely. An array of various embedded sensors can be deployed to assign a clinical parameter to a risk of a slip, trip, or fall event.
- Figure 1: Structure of the pressure sensor array. The system provides adequate data for balance ability analysis and simplifies the scoring process in balance tests, which improves medical professionals' work efficiencies. The proposed system is evaluated with standard balance tests (Limits of Stability, Unilateral Stance and Sit-To-Stance), whereas the data collected are analyzed with data mining techniques to verify the reliability of the designated process. Certain parameters are computed such as center of gravity, standard deviation, and sway velocities. The results show that the system is informational and reliable in the process of determining balance status during tests with additional advantages of simple procedures and efficient review communications.
- Figure 2: Diagram of the signal processing circuit board. Moreover, a pressure sensor array can be used to record a pressure distribution in gait analysis and/or tactile sensing applications. The pressure sensor array can include a piezo-resistive material and a uniform distribution of a plurality of flexible circuits. Each of the plurality of flexible circuits comprise at least one wire connecting an internal portion of a respective flexible circuit to a common port. A device housing the pressure sensor array can be trimmed to a size and used for a gait analysis and/or tactile sensing application. The arrangement of the wiring permits partial sensors to be used as part of the pressure sensor array during the gait analysis and/or tactile sensing applications.
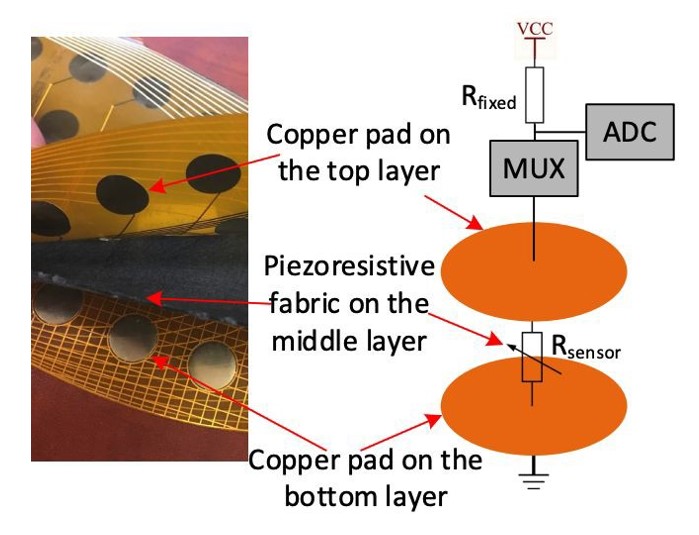 Figure 1: Structure of the pressure sensor array
Figure 1: Structure of the pressure sensor array
- The customized design makes it possible to meet the requirement on different sizes with only one design, which is cost effective and suitable for large scale production.
- The pressure sensor array with 96 pressure sensors provides high resolution pressure data, which contributes to the accuracy of the parameters measured by Wearable Gait Lab.
- Risk factors (awkward postures, over-exertions, and excessive repetitions) identification for work-related muscoloskeletal disorders (WMSDs)
- Workplace hazard (e.g. floor surface) improvement
- Indoor navigation (our current research)
- Gait rehabilitation
- Footwear and athletic performance
- Wearables (FitBit, Apple Watch, et al.)
- Rehabilitation outcomes management, e.g., orthopedic clinics and physical therapy
US Patent 10,918,312 issued February 16, 2021
Seeking development and licensing partners.
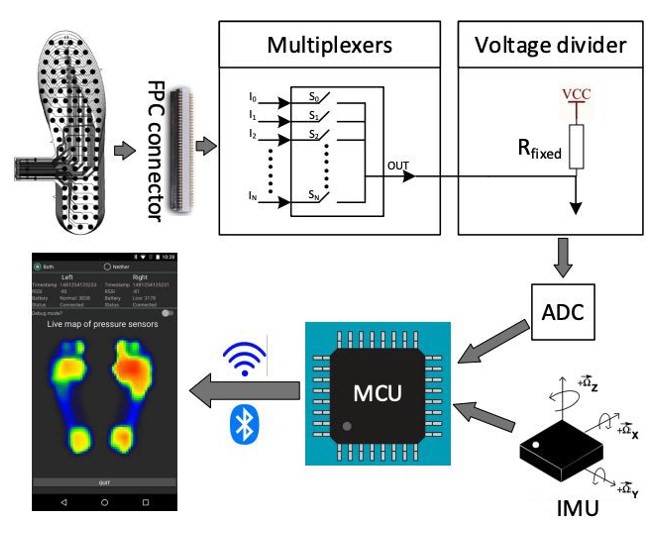 Figure 2: Diagram of the signal processing circuit board
Figure 2: Diagram of the signal processing circuit board
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
Patent Status |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |
|